4. The Earth and the Moon
The Moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth. Its surface is full of craters due to the impact of a huge number of meteorites. It neither have atmosphere nor
water.
The Moon is smaller than the Earth but is very close (384,000 km). This provokes two important phenomena: tides and eclipses.
It has two different movements:
-
Rotation
The Moon rotates around its own axis.
This movement takes 29.5 days to complete.
-
Revolution
The Moon moves around the Earth.
This movement takes about 29 days to complete.
The fact that these two movements take the same time, has as a consequence that we always see the same side of the Moon.
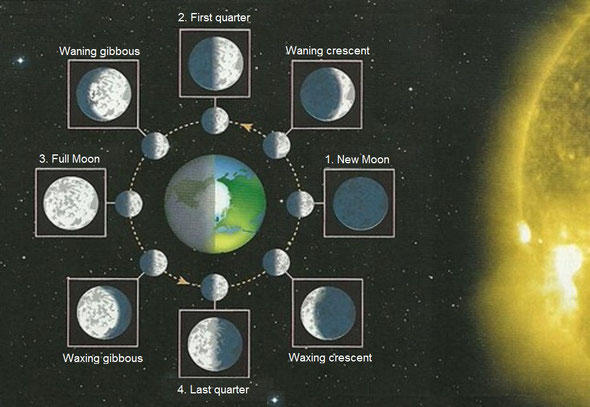
a) The phases of the Moon
The Moon is illuminated by the Sun. But it is not always in the same position, so that the aspect of the Moon saw from the Earth is different in different moments.
The several ways we can see it are called "phases of the Moon":
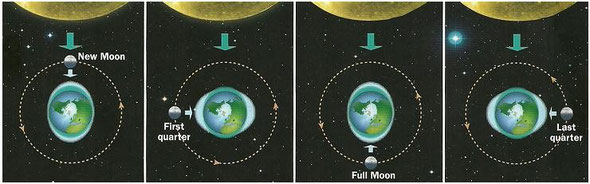
- New Moon. The Sun does not illuminate the Moon's side that faces the Earth.
- First quarter. The Sun illuminates the right side of the Moon. It is D-shaped.
- Full Moon. The Sun illuminates the whole Moon.
- Last quarter. The Sun illuminates the left side of the Moon. It is C-shaped.
b) Tides
Tides are periodic movements of the level of the sea due to the gravitational attraction that the Moon and the Sun have on the Earth.
- The level of water rises on the part of the Earth nearest the Moon
and in the opposite side too. It is called "high tide"
- The water level goes down on the rest of the Earth. It is "low tide"
Every place on the surface of the Earth changes twice a day, that is once every
12 hours, causing two high tides and two low tides.
- When the Earth, the Sun, and the Moon are in a line, the gravitational
forces of the Moon and the Sun add and the tides are larger.
This very high tide is called spring tide.
- When the Earth, the Sun, and the Moon are in angle of 90º,
the attractions of both are reduced a bit and the tides are smaller.
This tide is called neap tide.
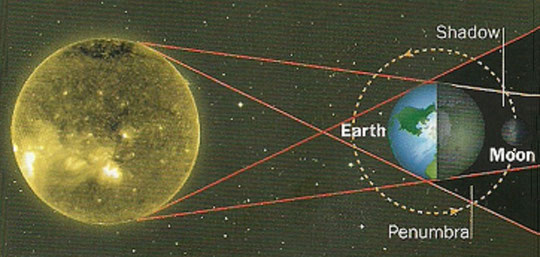
c) Eclipses
The Moon, the Earth and the Sun changes their relative position in the space because of their movements.
An eclipse occurs when the Moon or the Earth hide to the other one temporarily,
in a partial or in a complete way.
- Solar eclipse
The Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth projecting its shadow
onto the Earth.
- Lunar eclipse
The Earth is between the Sun and the Moon, projecting its shadow
onto the Moon.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
4.1. Answer the following questions:
a. Why can not we see the Moon during the period of "New moon"?
b. Which has more influence on tides, the Moon or the Sun? Why?
c. Why we always see the same side of the Moon?
d. When does an eclipse occur?
4.2. The following sentences are wrong. Correct them:
a. The Moon takes more time during its revolution than during its rotation
b. When in a place of the Earth it has high tide, in the opposite place
it has low tide.
c. Last quarter is the phase of the Moon between Full and New moon,
when we see the right side of del Moon illuminated.
d. A solar eclipse occurs when the Earth pass between the Sun and the Moon.
4.3. Listen and identify what phase of the Moon's cycle is described:
a. New moon
b. First quarter (Waxing moon)
c. Full moon
d. Last quarter (Waning moon)

Now,
check
your
answers!

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)