1. Fungi
Fungi are unicellular or multicellular organisms (without real tissues)
They have eukaryotic plant cells, but their cellular wall is made of chitin, not cellulose.
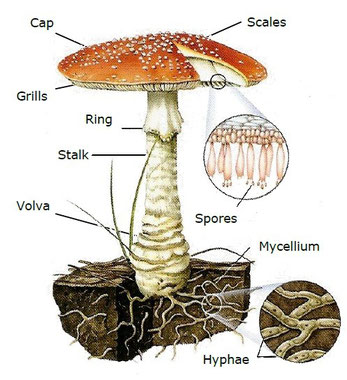
These cells are joined together forming threads, called hyphae. The vegetative body of fungus is the mycelium that is formed by the mass of hyphae. This mycelium lives under the soil.
a) Vital functions
Nutrition
Fungi are heterotrophs. They feed on organic matter. There are three types of fungi:
- Saprophytes. They feed on decomposed matter.
- Parasites. They feed on other living being that is harmed.
These fungi produce diseases.
- Symbionts. They live with other living being and both obtain benefits.
The most important symbiotic fungi are:
- Liquens (formed by a fungus and an alga)
- Mycorrhizas (formed by a fungus and a conifer)
Reproduction
They have sexual and asexual reproduction.
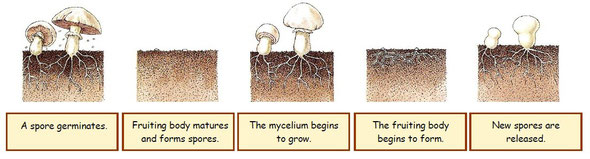
When they reproduce sexually, they produce spores.
When a spore germinates, it produces a mycelium that grows and produce a structure called the fruiting body (mushroom)
b) Classification
We can classify fungi in three groups without scientific value:

- Yeasts
They are unicellular fungi.
Many are parasites, but others are very useful for us.
Yeasts perform fermentation that transforms certain substances into food such us bread, wine and beer.
- Moulds
They are multicellular and microscopic fungi.
Many are parasites and others are decomposers,
such as bread mould or fruit mould.
- Mushrooms and toadstools
They are multicellular.
Some are edible (mushrooms) and other poisonous (toadstools)

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
1.1. Relate and order the pictures and the labels that correspond
to a fungus life cycle.
1.2. Listen and indicate which type of fungi is described:
a. Saprophytes
b. Parasites
c. Symbionts
1.3. Fungi and plants have eukaryotic plant cells. What characteristics allow
us to distinguish between them?

Now,
check
your
answers!
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)