2. Composition of living beings
All living beings are made up of the same chemical substances.
The most abundant chemical elements of living matter are: Carbon (C), Oxygen (O), Hydrogen (H), and Nitrogen (N) that make up about 95% of all living matter. But others elements, such as Calcium (Ca), Sodium (Na), Chlorine (Cl), Iron (Fe), Magnesium (Mg), among others, are also important. These elements are called bioelements.
Combinations of these elements form molecules of living matter called biomolecules. These biomolecules can be inorganic and organic.
a) Inorganic substances
lnorganic substances do not contain carbon.
They are present in living things and non-living things.
The main inorganic substances are mineral salts and water.
- Mineral salts have various functions:
- Solid: They make up different structures, like shells, bones
and teeth.
- Dissolved: They are present in internal fluids, like tears,
sweat and blood.
- Water is the most abundant substance in living things.
Water is necessary for chemical reactions and to transport
all other substances.
b) Organic substances
Organic substances are exclusive of living beings.
Carbon is their main element.
There are several types:
- Glucids (sugars or carbohydrates). Their function is provide
energy (e.g. glucose) and make structures such as plant cellular
wall (e.g. cellulose)
- Lipids. They are insulating and energetic reserve substances
(e.g. fatty acids) and they also make structures,
such as cell membranes (e.g. cholesterol)
- Proteins. They have several functions: transport substances
(e.g. haemoglobin transport oxygen), defense against
microorganisms (e.g. antibodies), help in chemical reactions
(e.g. enzymes), make structures (e.g. queratine forms nails
and hair), etc
- Nucleic acids. They control the cell's activity and contain
the inheritance information (e.g. DNA)

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
2.1. About the following chemical elements:
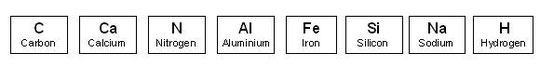
a. Classify them into chemical elements “typical of the living matter”
or “typical of the inert matter”
b. Which are the most abundant ones in the organic matter?
c. Which is the most representative one of the living beings?
d. What is the name of the group of elements which are characteristics
of organic matter?
2.2. Classify the biomolecules into organic and inorganic biomolecules.
What is the main difference between these two groups of molecules?
2.3. Join every biomolecule with its function:
a. Glucids
b. Lipids
c. Proteins
d. Nucleic acids
e. Water
f. Mineral salts
1. To contain the inheritance information
2. To give energy to the organism
3. To transport other substances through the body
4. To build structures, transport substances, etc.
5. To be reserve and insulating substances
6. To regulate chemical reactions, build skeletal structures
2.4. Listen and relate each sentence with a biomolecule.
a. Glucids
b. Lipids
c. Proteins
d. Nucleic acids
e. Water
f. Mineral salts

Now,
check
your
answers!
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




