3. The cell
Cells are the smallest units of life.
They are the structural and functional units for all living beings.
- All living things are made up of one or more cells.
- Cells carry out the functions of nutrition, interaction and reproduction.
- All cells come from other cells.
Most cells are very small. It is necessary a microscope to see them.
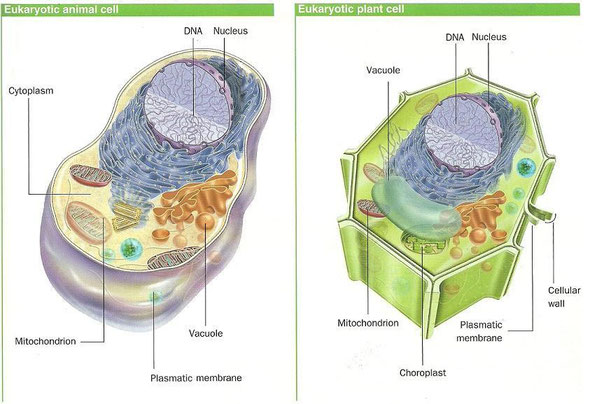
a) Structure of a cell:
Every cell has three main parts:
- The cell membrane covers the whole cell.
It is a thin layer of lipids that controls the pass of substances
in and out of the cell.
- The cytoplasm is the inside of the cell.
- It is a jelly-like substance. Many of the chemical reactions
of the cell take place here.
- It contains the organelles. They are small structures
responsible for respiration, making and storing nutrients, etc.
- The nucleus contains the DNA, the genetic material that forms
the chromosomes. Its function is to control and to regulate
how cell works. DNA contains the hereditary information
that is passed from one cell to the daughter cell.
b) Types of cellular organisation:
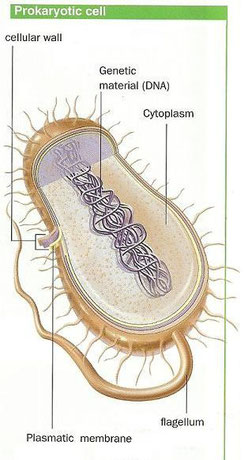
There are two kinds of cellular organisation: prokaryote and eukaryote.
- Prokaryotic cells
They are simple
They are much smaller than
eukaryotic cells.
Their genetic material is not separated
from the cytoplasm. They
don’t have a real nucleus.
They have a cell wall and flagellum
that allow them to move.
They only form unicellular organisms.
Bacteria have this kind of cells.
- Eukaryotic cells
They are complex.
They are bigger than prokaryotic cells.
Their genetic material is separated
from the cytoplasm into the nucleus.
They have many types of organelles
that make different metabolic jobs.
They form unicellular and multicellular
organisms.
They are the cells of all the rest of living
beings (fungi, protoctists, animals and
plants)
c) Types of eukaryotic cells
There are two types of eukaryotic cells: animal cells and plant cells.
Plant cells can be easily distinguished from the animal cells
because they have some exclusive organelles:
- They have cell wall, surrounding the cell membrane.
It gives the cell a polyhedral shape.
Its function is protecting the cell and being a skeleton structure.
- They have chloroplasts. Their function is to make photosynthesis
- They have a big vacuole that takes up the biggest part of the
cytoplasm. (Animal cells have vacuoles too, but they are smaller
and numerous) Its function is accumulating useless substances.
The plant cells are in algae and plants and the animal cells are
in animals and protozoa.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.1. Identify every one of the following cells and name the indicated
structures.
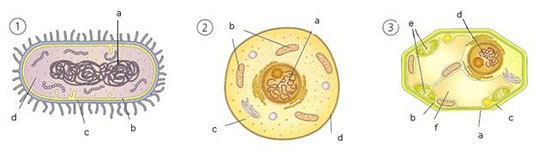
Now, listen and relate each definition with the correspondant cell's part.
3.2. Indicate if the following sentences are referent to animal cells,
plant cells or both:
a. They have mitochondria, the organelles which produce energy
b. They have ribosomes, little organelles that make proteins
c. They have a big vacuole that occupies the most part of the cytoplasm
d. They have plasmatic membrane, that controls the pass of substances
e. They have chloroplasts, which allow the photosynthesis
f. They have cellular wall, a rigid structure located outside
g. They have nucleus that contains the inheritance information
3.3. Answer these questions:
a. Is there any multicellular organism made up of prokaryotic cells?
b. What organelles are exclusive of plant cells?

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.

SPEAKING ACTIVITIES
Now, in turns with your partner,
answer the questions in the worksheet.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)