4. Molluscs
a) Habitat
Most part of Molluscs is aquatic. They live in the sea or in fresh water.
Some of them are terrestrial.
b) Morphological characteristics
- They have bilateral symmetry.
- They have a soft body divided into three parts:
- Head.
- Visceral mass with organs.
- Muscular foot with different shapes
depending on the group.
- The body is covered by a thick membrane, the mantle.
This produces a protective shell.
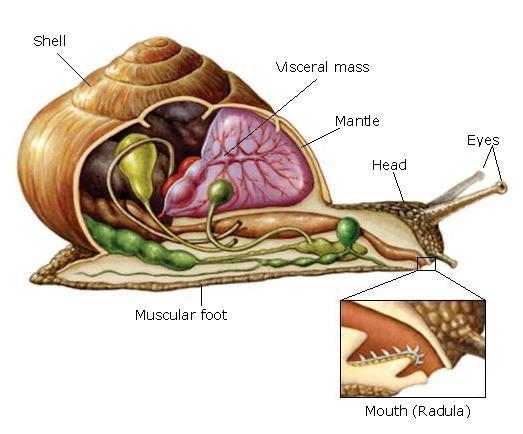
c) Vital functions:
Nutrition:
The digestive system has a mouth, anus and glands. They can be herbivorous and carnivorous.
Aquatic species breathe through gills, and terrestrial species breathe through lungs.
Molluscs have an open circulatory system. Blood exits from blood vessels to the tissues and then is collected by other blood vessels to return to the heart.
Interaction
They have a well developed brain and sense organs.
Reproduction:
Most are hermaphrodites and oviparous. Larva hatches and undergoes metamorphosis to become adult.
d) Classification:
- Gastropods (E. g. Snails, slugs and sea snails).
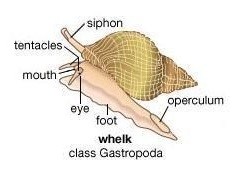
They are terrestrial and
aquatic animals.
They have a single spiral-shaped
shell, except slugs
that doesn’t have shell.
Their head is well-developed and has four tentacles and two of them have the eyes.
They are herbivores. The tongue (radula) is rasping.
They have a single muscular foot to move around.
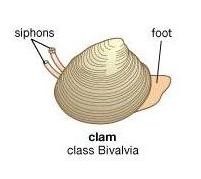
- Bivalves (E.g. Clams, cockles and mussels).
They are aquatic.
They have a shell with two valves.
They don’t have head.
They are filter feeders.
They have a single axe-shaped foot to excavate.
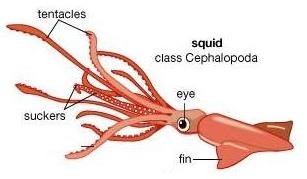
- Cephalopods (E. g. Octopus, squids and cuttlefish).
They are aquatic.
They have an internal shell, except octopus that doesn’t have it.
Their head is well-developed with big eyes.
Their foot is transformed into tentacles around the mouth, to catch prey.
They are carnivores. The mouth has a special chewing structure
called beak.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
4.1. Complete the chart about the main groups of Molluscs and classify
the molluscs that are represented.
Then, listen and indicate which sentece correspond to each group.
|
|
Gastropods |
Bivalves |
Cephalopods |
|
Foot |
|
|
|
|
Type of shell |
|
|
|
|
Environment |
|
|
|
|
Feeding |
|
|
|
|
Breathing |
|
|
|
|
Examples |
|
|
|

4.2. Listen and say which part of the Molluscs' body is described:
a. Head
b. Visceral mass
c. Muscular foot
d. Mantle
e. Shell

Now,
check
your
answers!

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.

SPEAKING ACTIVITIES
Now, in turns with your partner,
answer the questions in the worksheet.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




