6. Echinoderms
a) Habitat
All the animals included in this group are aquatic and marines.
They live on the sea bed, some fixed to substrate
and others move slowly about.
b) Morphological characteristics
- They have radial symmetry.
- Their body can have several shapes and it is formed by five equal sections.
- They have an internal skeleton (under the skin) made of plaques of calcium
carbonate, called dermal skeleton. Usually they have spines too.
- They do not have a differentiated head.
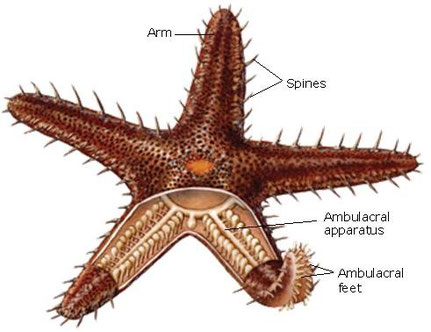
c) Vital functions
Nutrition:
The digestive system has mouth, anus and glands. They are carnivorous.
They have an exclusive system called ambulacral apparatus.
It consists on a series of tubules filled with sea water
that end in ambulacral feet with suckers. It has several functions: locomotion, breathing, circulation and excretion.
Interaction:
They do not have a well-developed nervous system: neither brain nor complex sense organs.
Reproduction:
They have sexual reproduction. Most have separated sexes and some are hermaphrodites.
Fertilization is external.
They are oviparous.
Larva hatches and undergoes metamorphosis to change into adult.
Some species have regeneration power. This is the capacity to develop again lost body parts.
d) Classification

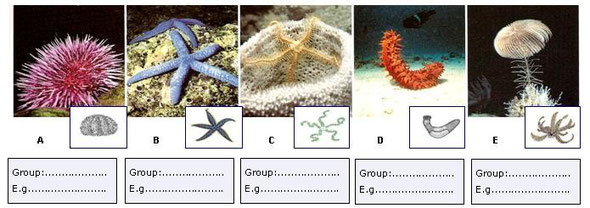
- Asteroidea (E. g. Starfish)
They are star-shaped with five arms.
They are carnivorous.
- Echinoidea (E.g. Sea urchins)
They are rounded-shaped and long spines.
They are herbivorous.
- Ophiuroidea (E. g. Brittle stars)
The are star-shaped, with very long
and flexible arms.
They are filter feeders.
- Crinoidea (E.g. Sea lilies)
They live attached to substrate
and they are feathery-shaped.
They are filter feeders.
- Holothuridea (E.g. Sea cucumbers)
They are cylindrical-shaped.
Their mouth is surrounded by tentacles.
They eat plankton.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
6.1. Answer the following questions about Echinoderms:
a. What is the dermal skeleton? What is it made up? Where is it located?
b. What is the ambulacral apparatus? What are its functions?
6.2. There are five groups of Echinoderms. Can you identify them
among the pictures?
6.3. Listen and indicate which characteristic of Echinoderms is described:
a. Radial symmetry
b. Ambulacral apparatus
c. Dermal skeleton

Now,
check
your
answers!

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.

SPEAKING ACTIVITIES
Now, in turns with your partner,
answer the questions in the worksheet.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)



