2. The human cells
The cell is the structural and functional unit of living beings. It is the living being’s smallest part which is able to carry out the vital functions: nutrition, interaction and reproduction.
Human cells are eukaryotes (with true nucleus).
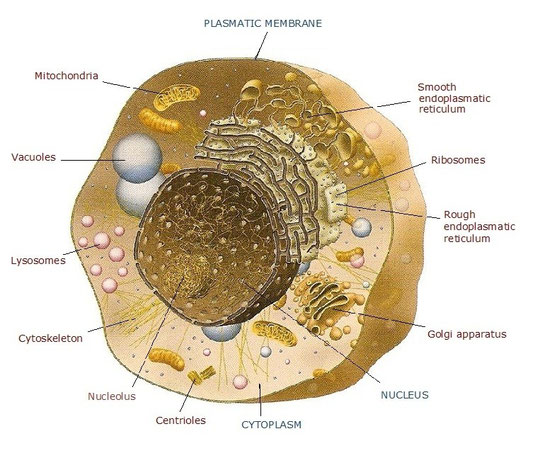
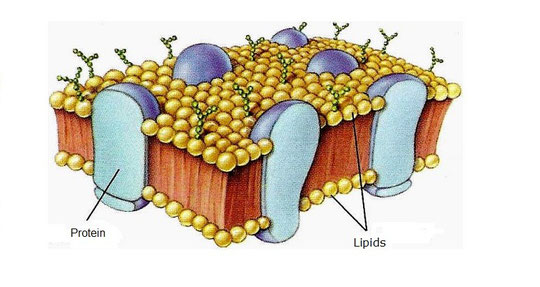
a) Plasmatic membrane
It is a thin layer which involves the cell, protects it and controls the pass
of substances (nutrients and wastes) in and out of cell.
It is mainly made by lipids and proteins. The lipids form a double layer
in which proteins are included. All cellular membranes have this structure.
b) Cytoplasm
It is the space between the nucleus and the plasmatic membrane.
It is made of water with numerous dissolve substances.
It contains the organelles.
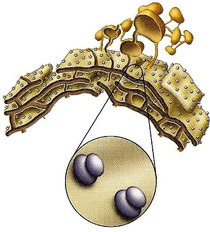
- Endoplasmatic reticulum
Group of membranous sacs and canals
communicated each other
and which extends through the whole
cytoplasm.
It makes different substances, like proteins
and lipids that form the cellular membranes.
There are two types:
- Rough endoplasmatic reticulum
(with ribosomes attached)
- Smooth endoplasmatic reticulum
- Ribosomes
They are little organelles that can be free in cytoplasm or attached to RER.
They are made of DNA and proteins and do not have membrane.
Their function is to make proteins
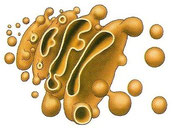
- Golgi apparatus
It is formed by membranous sacs and vesicles.
It process the substances made by the ER
and produces secretions and lysosomes

- Lysosomes
They are membranous vesicles which contains digestive
enzymes. Their function is the cellular digestion

- Centrioles
They are two tubes of protein.
They control the cell movement
and the movement of the other organelles
within the cell.

- Cytoskeleton
It’s a protein filament net
which is through the whole cytoplasm.
It gives form to cell and make able
the movement of organelles inside it.
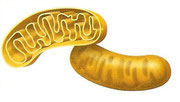
- Mitochondria
They are organelles with a double membrane.
Their function is cellular respiration
that provides energy to cellular metabolism.

- Vacuoles
They are membranous vesicles which contains different
substances (water, nutrients or wastes)
c) Nucleus
It is a spherical structure formed by nuclear membrane that protects
chromatin. Chromatin is the genetic material which controls the cellular
functions. It is made by DNA and proteins. During cell division chromatin
condenses and packs to form the chromosomes.
Inside the nucleus it is also the nucleolus, an organelle made by RNA
and proteins, which makes ribosomes

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
2.1. Explain the meaning of this sentence:
«Cells are the anatomical and physiological units of living beings».
2.2. Classify the organelles into membranous (made by cellular membrane)
and non-membranous.
2.3. What is the difference between chromatin and chromosome?
2.4. Listen and indicate what organelle is described:
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




