3. Diets
Most types of foods contain different nutrients in different proportions.
For this reason, you shouldn't eat all types of food in equal quantities or equally frequently.
The diet is the quantity and type of food a person consumes daily.
This food pyramid is a summary of the recommended intake of different foodstuffs.
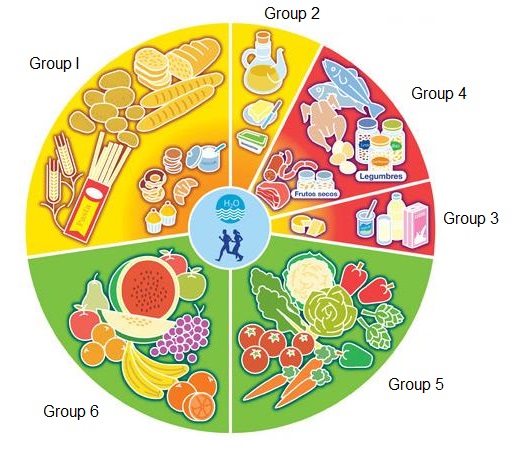
Food is classified into seven groups, based on the type of nutrients it contains which is known as nutritional value.
- Group I: cereals and derivatives, potatoes and sugar.
Nutritional value: glucids and minerals.
- Group II: butter, fats and oils.
Nutritional value: lipids and liposoluble vitamins.
- Group III: milk and its derivates (dairy products).
Nutritional value: protein, lipids, vitamins and minerals.
- Group IV: meat, fish and eggs, legumes and dry fruits.
Nutritional value: protein.
- Group V: vegetables.
Nutritional value: water, fibre, vitamins and minerals.
- Group VI: fruits.
Nutritional value: water, fibre, sugars, vitamins and minerals.

Food groups can be represented into a food wheel. It is a diagram which shows us the function of each group in the body.
- The red segments (Groups 3 and 4) are mainly structural.
- The green segments (groups 5 and 6) include food with regulatory function
- The yellow segments (groups 1 and 2) have energetic function.
3.1. The good diet
To develop a healthy life is very important that our diet were adequate to our style of life, sex, age. But moreover, a good diet must be:
- Complete: It has to include foods of every group.
- Varied: It has to include different food of each group.
- Balanced: It has to give us all the nutrients we need and in the correct proportion and quantity.
We can follow some advice to get it, which involves not only the kind of food we must eat, but also the way in which we must eat them.
- Balance the amount of energy we take every day.
Not to eat too much sweets and fats.
- Eat of everything. As often as we can it is better consume
fresh food.
- Make 4 or 5 meals a day, do not miss out any meal and try to make
them in a regular hour.
- It has to provide us with enough protein content. They are preferable
fish (better blue fish) and pulses, instead of red or too fatty meat.
- It has to include food rich in vitamins and minerals and fibre.
It is recommendable to include 5 servings of fruit and vegetables at less.
- Drink mainly water, at less 2 litres per day, avoiding alcoholic
or too many sweet drinks.
A good example of a good diet is the Mediterranean diet.
The Mediterranean dietrefers to traditional food from countries in southern Europe, like Spain. It is considered to be one of the most balanced and healthy diets in the world.
The basic foods in a Mediterranean diet are olive oil, cereals, pulses, vegetables, fish, and fruit.
The Mediterranean diet helps protect us against circulatory diseases caused by too much cholesterol in the blood. It also helps prevent constipation, colon cancer and obesity, among other things.
Animación: La dieta mediterránea
Infografía: La dieta mediterránea (Consumer Eroski)
3.2. Special diets
It is not always possible to follow advice and have a balanced diet. Disorders and illnesses may mean we have to stop eating or eat more of certain types of food.
There are different types of special diet:
- Low- or high-calorie diets. They have either a lower or higher percentage of energy-rich food. They are recommended for people who have to loss or win weight.
- Low-cholesterol diets. These are recommended for people
who have circulatory problems.
- High-fibre diets. These have a large quantity of food rich in fibre. They are recommended for people who suffer from chronic constipation.
- Low-fibre diets. These contain very little fibre so are recommended for people who have an intestinal obstruction or slow intestinal movements.
We can also find different dietary habits in different countries.
These differences are due to cultural tradition, the availability of certain
products and for hygienic or religious reasons.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.1. Copy and complete the following table. Classify food into its group,
indicate what kind of nutrients give us each group and what function
they have.
|
|
GROUP I Milk and its derivates
|
GROUP II Meat, fish and eggs |
GROUP III Pulses, root vegetables and dried fruits |
GROUP IV Vegetables |
GROUP V Fruits |
GROUP IV Cereals and sugar |
GROUP VII Fats and oils |
|
Food |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nutritional value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Function |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.2. What characteristics have to have a good diet?
What advice could you give to follow it?
3.3. Why it is said that the Mediterranean diet is one of the best diets
in the world? Elaborate a set menu characteristic of this diet.
It has to include a breakfast, a morning snack, a lunch,
an afternoon snack , and a dinner. Do not forget drinks.
3.4. Listen to two friends getting luch at a buffet.
a. Who is eating a more mediterreanean diet?
b. What are the foods could be added to that person's mediterrenean diet?
3.5. What the differences are between:
a. A low-calorie diet – High-calorie diet
b. A high-fibre diet- Low-fibre diet
3.6. Fad diets promise dramatic weight loss. Listen to the descriptions
of three of these diets, make notes and complete the chart:
|
|
|
Dukan diet |
Paleo diet |
5:2 diet |
|
How it works |
|
|
|
|
|
Pros |
|
|
|
|
|
Cons |
|
|
|
|
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




