3. The respiratory system
In addition to the nutrients obtained by digestive processes, our cells also need oxygen to live. This oxygen is used to perform cellular respiration, a metabolic reaction that takes place in every one of the body cells.
Cellular respiration is the combustion of organic matter with the help of oxygen to obtain energy to carry out the vital functions. This process occurs in mitochondria and produces, as a result, water and carbon dioxide.

Respiratory system assures that this oxygen goes from the air to the blood that will carry it to every cell, and that the carbon dioxide produced by them, will be expelled. This process is called ventilation (breathing).
So that, in fact, respiration is the joint of two processes: ventilation and cellular respiration.
We can distinguish two parts in the respiratory system:
- Airways. The joint of conducts through which air circulates
(nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles)
- Lungs. Organs where is produced the exchange of gases.

a) Airways:
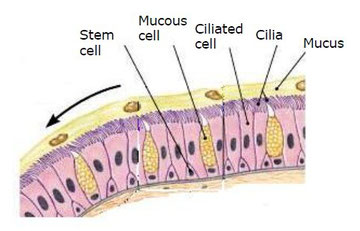
Airways are covered by an epithelium formed by ciliated cells and mucous cells. Its function is to humidify the air and to clean it.
The mucus traps the strange particles (like dust, pollen or microorganisms) which air can carry, to avoid that they can pass to lungs.
The cilia force the mucus to the pharynx and from here it passes to the oesophagus to be digested. In addition mucus has a large amount of water and part of it, is added to the air.
Respiratory passages are:
- Nasal cavity. It is divided in two chambers. Every one of them has an external opening (nostril) and an internal opening to pharynx (choane). The nostrils are covered by the nose. Nasal cavity has many nooks and it is lined by the pituitary membrane. This epithelium has a large number of surface blood capillaries . Their function is to warm the air. In the most upper zone of nasal cavity are the olfactory receptors which function is to detect the smell.
- Pharynx. It is a duct shared with the digestive system. We can find here several openings: choanae, glottis and Eustaquian tubes (that connect with middle ear)
- Larynx. It is a short and cartilaginous tube. Its entry (glottis) is regulated by the epiglottis to avoid the entry of food. Within the lumen of larynx are the vocal folds which produce the voice sounds when vibrate.
- Trachea. It is a tube about 12 cm long and 2.5 cm in diameter. Trachea has a cartilaginous skeleton made of incomplete rings of cartilage which keeps the conduct open and assure the entry and the exit of air.
- Bronchi. They are the two branches trachea is divided into. Each bronchus enters in a lung. As trachea, they have a cartilaginous skeleton.
- Bronchioles. Every bronchus is divided several times in progressively thinner tubes (bronchioles). The thinnest bronchioles do not have cartilaginous skeleton and end in alveoli.
b) Lungs:
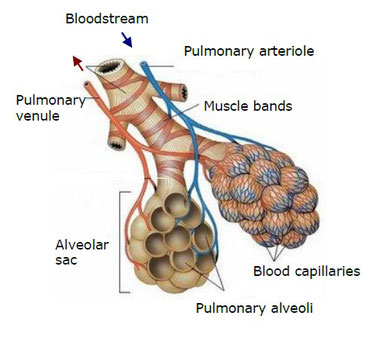
They are two pinkish and soft organs that occupy most of the thoracic cavity. They are made of alveoli and the thinnest bronchioles.
Alveoli are very small sac-shaped structures, surrounded by a dense network of blood capillaries. Here is performed the exchange of gases between blood and air.
Each lung is divided in lobes. There are three lobes in the right lung and only two in the left one.
Surrounding the lungs there are two membranes called pleurae. In the space between them there is a liquid that allow them move one close the other. Functions of pleurae are to protect the lungs from the friction with ribs, and help in ventilation.

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.1. Explain why:
a. the nasal cavity has so many nooks.
b. it is recommended breathing through the nose and avoid do it through the mouth.
c. we produce a large amount of mucus when we catch a cold.
d. the left lung is smaller than the right lung, and has only two lobes.
3.2. Listen and complete the text. What process is been described?
|
The cells in our body require........................ This ......................... is essential for cellular ............................ This process uses ......................... and turns it
into .....................
|
3.3. Listen and indicate which structure is related each sentence.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




