4.2. The urinary system
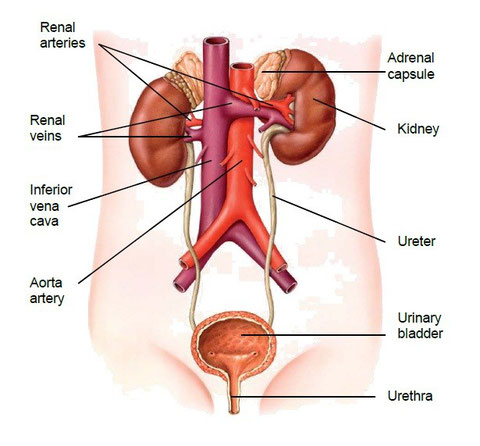
The urinary system is formed by kidneys and urinary tracts.
a) Urinary tracts
They are the ducts which collect and lead to the urine out of the body.
- Ureters: Two thin and long tubes which connect the renal pelvis
to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary bladder: It is a muscular and elastic bag which stores
urine.
- Urethra: It is the conduct which connects the bladder to
the exterior. It has a sphincter that controls the exit of urine.
In men the urethra is shared with the reproductive system and
cross along the penis. By contrast, in women it is a
shorter independent tube.
Kidneys produce urine continuously. This urine is stored into urinary bladder
until it is full. Miction is the act to evacuate this urine from the body.
b) Kidneys:
They are two bean-shaped organs about 11 cm long, 5 cm wide and 3 cm thick.
They are located both sides of spinal column in lumbar region in the abdominal
cavity. The right one is slightly lower due to the fact that the liver is above it.
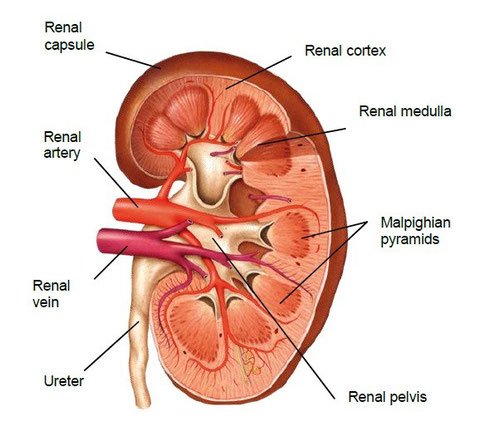
In a transversal cut, we can distinguish:
- Renal cortex: It is the outer portion. It has a granular shape.
- Renal medulla: It is the middle layer. It has a fibrous shape and
is divided into portions called malpighian pyramids (or renal pyramids)
- Renal pelvis: It is the internal cavity of kidney which connects
with the ureter.
Each kidney is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called renal capsule and by a layer of adipose tissue that protects it from shock.
On the top of kidneys are located the adrenal capsules which are endocrine organs. They really do not form part of kidneys, only are attached to them.
Each kidney is irrigated by a renal artery and a renal vein which are branches of aorta artery and inferior vena cava respectively.
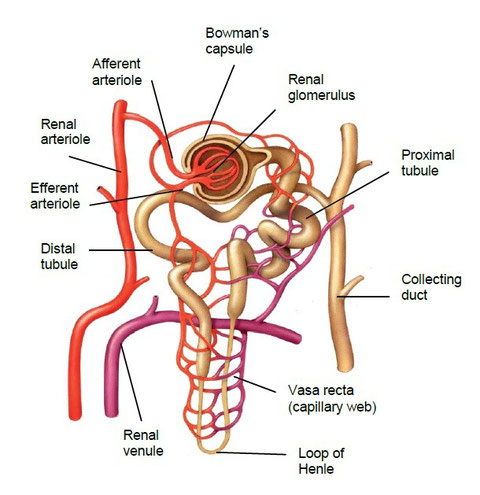
Nephron is the basic anatomical and physiological unit of the kidney.
Each kidney is formed by about a million of nephrons.
A nephron is a blind-ended tubule with a complex structure:
- Renal corpuscle
- Bowman’s capsule à Cup-shaped structure
with double wall in which central cavity
is located the renal glomerulus.
- Renal glomerulus à Capillary network.
- Renal tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
Each nephron connects with a collecting duct which collects the urine
produced by many nephrons and carries it to the renal pelvis.
Blood arrives to glomerulus from an afferent arteriole and exits from it
through an efferent arteriole. Arterioles can keep the blood flows to
high pressure. This help in filtration of blood. Surrounding the renal
tubule there is a dense capillary web called vasa recta.

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
4.1. What are the waste substances produced by our organism?
Indicate the origin and the way of excretion of each one.
4.2. Why do babies need nappies?
4.3. What could happen if we would not have urinary bladder?
4.4. Listen and indicate which part of the urinary system is described:
a. Kidney
b. Ureters
c. Urinary bladder
d. Urethra
4.5. Listen and complete the text:
|
The …………………….
This is the …………………… part of the kidney. It is formed by the …………………………….., which surrounds the …………………….............…., an accumulation of ................................. from the ...............................
The Bowman's capsule extends into the …………………………., a tube surrounded by capillaries that leads into the ………………………….
Collecting ducts empty .................... into the ..................................
|
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




