3.1. The spinal cord
This is a thin nerve tube about 45 cm long that is located inside the vertebral column.
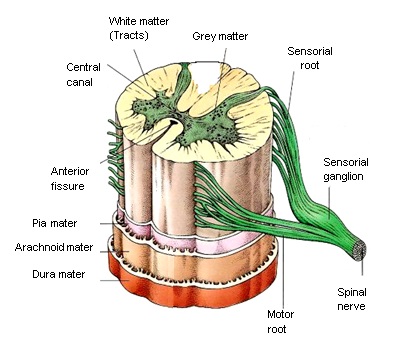
- White matter is on the outside of the spinal cord and it is formed by ascending and descending bundles of axons, called tracts.
- Grey matter is on the inside and it is shaped like the wings of a butterfly.
In the centre of the spinal cord there is the central canal (or ependyma) which is an anatomic extension of the spaces in the brain known as the ventricles and, like the ventricles, contain cerebrospinal fluid.
Pairs of spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord to the right and to the left. Each one has a sensory root attached to the posterior or dorsal horn of the grey substance and a motor root attached to the anterior or ventral horn. These two roots join then to form the spinal nerve.
The functions of the spinal cord are:
- To transmit the sensorial impulses from sensorial nerves to the encephalon and the motor impulses from the encephalon to the motor nerves. It is the connection between the encephalon and the body.
- To carry out the reflex responses for some sensory impulses directly, without the encephalon participation.
A reflex action is an automatic and unconscious reaction produced as response to a specific stimulus. The cerebral cortex is not involved in this type of nerve actions.
Reflex acts are related with the survival. For example if you feel that something can enter in your eye, you close it without think about it. Or if you burn your hand you retire it immediately, before you will be conscious of what has happened.
Three types of neurons participate in reflex actions. They form the reflex arc.
- A sensory neuron that comes from a receptor and enters into the spinal cord through its sensory root.
- An interneuron that connects with the sensory neuron and transmits the impulse to the motor neuron.
- A motor neuron that exits from the spinal cord by its motor root and arrive to a muscle.


ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.3. Listen and find the six mistakes in the text:
|
The spinal cord
The spinal cord is a short, thin tube made up of muscle tissue protected by the skull, which links the encephalon to the rest of the body.
It serves as a conduit for nerve impulses from the effectors to the encephalon and from the encephalon to the receptors.
It also coordinates simple responses called voluntary actions.
|
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




