3.2. The encephalon
The encephalon or
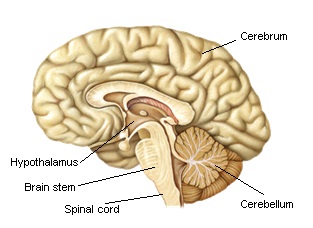
brain is formed by several nerve centres. The most important are the cerebrum, the cerebellum and the brain stem.
a) The cerebrum:
It is the largest part of the encephalon and the main nerve center.
Grey matter is located on the outside and white matter on the inside. Grey matter is called the cerebral cortex. It is a very thin layer (only about 2 mm thick). It is divided in three functional areas: motor, sensory and association cortex.
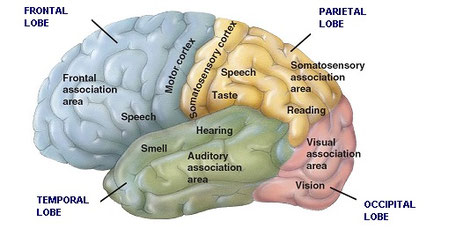
The cerebral cortex is full of folds and furrows. These folds divide the cerebrum surface in:
- Circumvolutions (or gyri). They are more numerous and less deep lines.
- Fissures (or sulci). They are less numerous and deeper lines.
Fissures divide the cerebrum in lobes. Each lobe receive the name of the cranial bone under it is situated (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes). Each zone has a function. The main fissure (great longitudinal fissure) divides the organ in two cerebral hemispheres. Their functions are different:
- Intuitive and creative capacities are located in the right hemisphere.
- Logic and analytic capacities are located in the left hemisphere.
Cerebral hemispheres are joined by a structure called corpus callosum that allows the coordination between them and with other parts of CNS.
Cerebral cortex functions are many and very important:
- It receives and processes the sensory information, except the balance.
- It controls and coordinates all parts of the body.
- It develops the higher nerve functions (memory, reasoning, intelligence,
conscience and will)
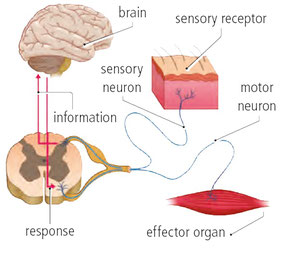
- It controls the voluntary and conscious movement (voluntary actions)
In voluntary actions the response is generated consciously in the cerebral cortex.
The limbic system is other important part of the cerebrum. It includes several structures. Hypothalamus is the most important. It is located between the brain stem and the cerebrum.
Their functions are:
- To regulate the function of the endocrine system through the hypophysis.
- To be responsible for emotions, feelings (love, hatred, sadness, happiness, fear, etc.) and basic instincts such as hanger, thirst and sexual desire.
b) The cerebellum
It is located under the cerebrum in the occipital zone.
Its external shape is similar to cerebrum. Its surface is folded and it is divided into two cerebellar hemispheres, although in this case appears other central protuberance, the vermis.
Grey matter is on the outside and white matter is on the inside and is tree-shaped.
The functions of cerebellum are:
- It receives and processes the sensory information of balance.
- It controls the balance and the posture.
- It coordinates the movements to assure that they are precise and harmonic.
c) The brain stem
It includes several parts of the encephalon between the spinal cord and the cerebrum.
The most important part of the brain stem is the medulla.
The medulla is a bulky prolongation of the spinal cord. Its surface is smooth and uniform. White matter is on the outside and grey matter is on the inside.
Nervous bundles which come from the spinal cord cross in the medulla (decussation). As a result, the left cerebral hemisphere controls the right side of the body and the right hemisphere controls the left side.
The medulla is responsible for several automatic and vegetative functions like heartbeat, breathing rate and blood pressure and it is also involved in some reflex acts such as coughing or vomiting.

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.4. Why do you think that the cerebral cortex is so much folded?
3.5. Indicate which part of the CNS is the responsible for these actions:
§ To resolve a math problem § To talk to a friend
§ To ride on bicycle § To keep the cardiac rhythm
3.6. Listen and say to which part of the encephalon correspond each
sentence:
a. Cerebrum
b. Cerebellum
c. Medulla
3.7. Listen to the sentences and decide if they refer to voluntary
or involuntary actions.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




