5. The endocrine system
The endocrine system is the other coordination system of the body. It is closely related with the nervous system and they depend on each other. Sometimes the nervous system stimulates or inhibits the secretion of a hormone, and other times hormones stimulate or inhibit the action of the nervous system.
They control different situations because their characteristics are different too:
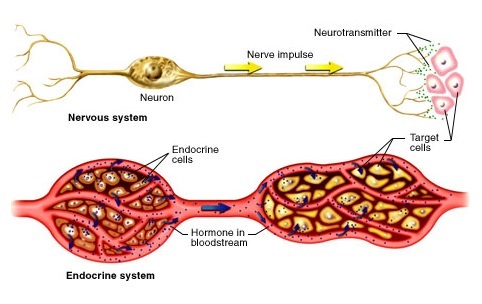
- The nervous system transmits the information through the nervous impulse
that is an electrical signal while endocrine system transmits the information
through hormones that are chemical substances.
- Nervous impulse passes from neuron to neuron, while hormones are carried by
bloodstream.
- The nervous system acts quickly (milliseconds) and its actions are short in time.
Usually this action ends when stimulus disappears. In contrast, the endocrine system
acts slowly (from seconds to days) and its actions are lasting in time. Usually
this action continues although the stimulus disappears.
- The nervous impulse has local effects while hormones have general effects
that many times affect to all the body.
The functions controlled by the endocrine system are:
- Reproduction
- Growth and development
- Mobilisation of body defenses
- Maintenance of homeostasis
- Regulation of metabolism
The endocrine system is formed by several glands (endocrine glands) distributed through all the body and that are not connected to each other. These glands produce substances (hormones) that are released directly into the blood.
A hormone is an organic chemical substance that controls the activity of an organ.
- Each hormone exerts its action only over a determine cell type (target cell).
- It is necessary only a very little amount of hormone to assure its effect.
- They are only produced when and during the time that it is necessary.
- They are only produce in the optimal amount.
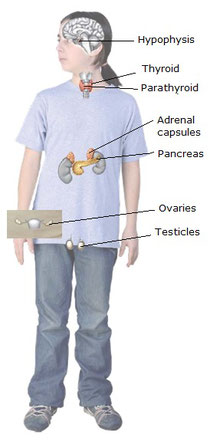
The main endocrine glands are:
- Hypothalamus. It is situated in the basis of encephalon and is attached to the hypophysis.
- Hypophysis (or pituitary gland). It is a little gland situated in the encephalon.
- Thyroid. It is located in the neck under the larynx and behind the trachea.
- Parathyroid. It is formed by four small glands attached to the thyroid.
- Adrenal capsules. Two glands located on the kidneys.
- Pancreas. It is a mixed gland because it has
two types of secretion, a digestive juice (pancreatic juice) and a hormonal secretion.
- Gonads. They are testicles (males) and ovaries (females). They are mixed glands too because they produce gametes (ovules and spermatozoids) in addition to hormones.
The main hormones produced by each one are:
- Hypophysis (pituitary gland)
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) reduces the water amount eliminated by urine.
- Oxytocin stimulates uterus contractions during labour and milk ejection
in mammary glands.
- Stimulating hormones provoke the secretion of other glands (gonads, thyroid
and adrenal capsules)
- Somatotropin. It is the growth hormone. Provoke the enlargement of bones
and general growth of body.
- Thyroid
- Thyroxine regulates the metabolism
- Calcitonin reduces the blood calcium levels and provokes its deposition
in bones.
- Parathyroid
- Parathyroid hormone regulates the levels of calcium and phosphorus
in blood.
- Adrenal capsules
- Adrenalin prepares the organism for action.
- Corticoids control several metabolic processes and water amount in tissues.
- Aldosterone regulates the sodium and potassium concentration in blood.
- Pancreas
- Insulin increases the use of glucose by tissues and muscles
(reduces the glucose in blood)
- Glucagon provokes the transformation of glycogen from liver into glucose
(increases the glucose in blood)
- Ovaries
- Oestrogens produce and maintain the secondary sexual characters.
- Progesterone allows the embryo implantation into uterus.
- Testicles
- Androgens produce and maintain the secondary sexual characters.

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
5.1. Hormones are called many times “chemical messengers”.
What does it mean?
5.2. What hormone will be secreted when:
§ Your body is dehydrated and you cannot drink water.
§ You have just eaten and the glucose levels in blood are high
§ You are excited and nervous because you are in danger.
5.3. Listen and indicate what endocrine gland is described.
Which are missing?
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)



