3. Physiology of reproduction
3.1. Formation of
gametes
Gametes are formed by a process called gametogenesis.
This process takes place in gonads (ovaries and testicles).
Gametes form from germ cells which like other human cells have 46 chromosomes. However when gametes are formed the number of chromosomes is halved through a special type of cell division called meiosis. The resulting cells therefore only have 23 chromosomes.
a) Spermatogenesis
This is the male gametogenesis. It takes place in the walls of the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
The process takes about two months and after puberty it occurs continuously throughout the man’s lifetime. Spermatozoa are produce in large quantities (millions) each day.
After meiosis the cells become spermatozoa, male gametes, through a process of cellular specialisation during which they change their shape.
- They reduce their volume
- The organelles disappear except the nucleus and the acrosome.
- The flagellum develops.
A spermatozoon has three parts:
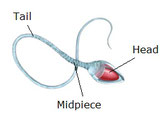
- Head. This contains the nucleus (genetic material) and the acrosome (organelle that contains digestive enzymes to dissolve
the outer layer of the ovum)
- Midpiece. This part is located between
the head and the tail. It contains lots of mitochondria that provide the energy
required to move the flagellum.
- Tail. It is a flagellum which enables
the spermatozoon to move.
b) Oogenesis
This is the female gametogenesis. It takes place in ovaries, inside structures called follicles.
After puberty, oogenesis takes place regularly in woman, approximately every 28 days. An ovum develops, mature and is released each time.

As spermatozoa, ova change after meiosis to become a specialised cell. Its size increases because of the accumulation of nutritive substances which will be the support of the embryo during the first few days after fertilisation.
In addition, ovum is covered by two protective layers the zona pellucida (mucous substance) and the corona radiate (remains of follicular cells).

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.1. Answer these questions:
a. How do ovum and spermatozoon differ?
b. What are the differences between the production of male and female
gametes?
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




