2.3. Circulation
Once nutrients and oxygen have been absorbed, it is necessary carry them to every cell of the body.
The simplest animals (Poriferans and Cnidarians) do not need a circulatory system because most part of their cells is in contact with the external medium and the exchange can be direct.
The rest of animals need a distribution system which assure the transport of useful substances from the absorption organs to every cell and of useless substances from cells to the excretory organs.
a) Components of the circulatory system:
The circulatory system is made up of:
- Transport liquid.
It is a fluid which flows within the body carrying nutrients and wastes.
Echinoderms have hydrolymph and Arthrophods have hemolymph.
Vertebrates and Annelids have blood. Blood is composed by water
with different substances (blood plasma) and different kinds of cells:
- Red blood cells (they transport oxygen)
- White blood cells (they defend the body against infection)
- Platelets (they coagulate the blood)

- Vessels.
They are the ducts through which the transport liquid flows.
Vertebrates have three types:
- Arteries. They are the vessels through which blood exits from the heart.
- Veins. They are the vessels through which blood enters into the heart.
- Capillaries. They are the smallest vessels of very thin walls, through
which substance exchange is made between blood and tissues.

- Heart.
It is muscular organ which pumps the transport liquid.
It is a simple vesicle in Invertebrates and has several chambers in
Vertebrates.
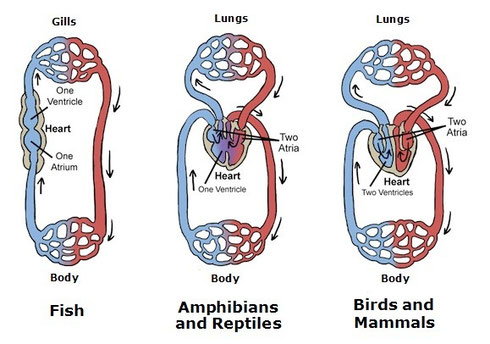
- Fish’s
heart has an atrium and a ventricle.
- Amphibians and Reptiles’ heart has two atria and one ventricle.
- Birds and Mammals’ heart has two atria and two ventricles.
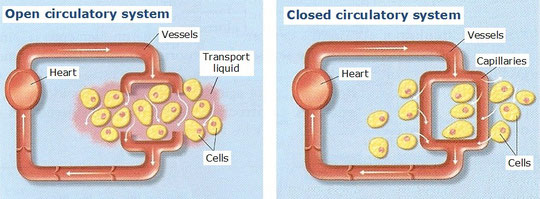
b) Types of circulatory system:
There are two kinds of circulatory systems:
- Open circulatory system.
It is characteristic of mostof the invertebrates, such as Molluscs
and Arthropods.
Vessels do not form a close circuit. There are not capillaries.
Hemolymph exits from the vessels to the tissues, where the substance’s exchange is made directly between the cells and the transport liquid and then, it is pick up by other vessels and returns to the heart.
- Closed circulatory system.
It is characteristic of Vertebrates, Annelids and Cephalopods (octopuses, squids, etc)
Blood vessels form a closed circuit. Blood never exits of them.
Substance exchange is made between the cells and the blood through the capillaries.
In Vertebrates, the circulatory system can be simple or double:
- Simple closed circulatory system.
Blood passes through the heart once, completing one loop.
The blood goes from the heart round the body, passes through
the gills, where it is oxygenated and then returns to the
heart.
It is the circulatory system of Fish.
- Double closed circulatory system.
Blood passes through the heart twice, completing two loops:
- Pulmonary or minor circulation.
The blood goes from the heart to the lungs where it picks up
oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
Then it returns to the heart.
-
Systemic or major
circulation.
The blood goes from the heart to the body bringing oxygen to
the cells and collecting carbon dioxide from them.
Then it returns to the heart.
Amphibians and Reptiles have a heart with only one ventricle
where oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mix.
They have incomplete circulation.
In contrast,
Birds and Mammals which heart has two ventricles,
has complete circulation because the oxygenated blood never mixes
with the deoxygenated blood.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
2.9. Which are the circulatory system functions?
2.10. Which are the components of a circulatory system?
2.11. What is the difference between:
a. Arteries – Veins
b. Closed circulatory system - Open circulatory system
2.12. Explain why:
a. Insects have a very little developed circulatory system
b. It is said that frogs have incomplete circulation
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)





