2. Terrestrial ecosystems
A biome is a large area on Earth where ecosystems share a similar climate and dominant vegetation, and also therefore have a typical fauna.
The distribution of these biomes mainly depends on the climate and climate depends on:
- Latitude: the higher the latitude, the lower the temperature. On average,
atmospheric temperature decreases by 0.5 °C for every degree that latitude increases.
- Altitude (height above sea-level or elevation): the higher the elevation, the lower
the temperature.
On average, atmospheric temperature decreases by 1°C for every 180 m
of elevation.
The type of biome depends on the temperature, so similar biomes are found at low elevations and at low latitudes, for example, tropical rainforests. In the same way, similar biomes are found at high elevations and at high latitudes, for example, tundra.
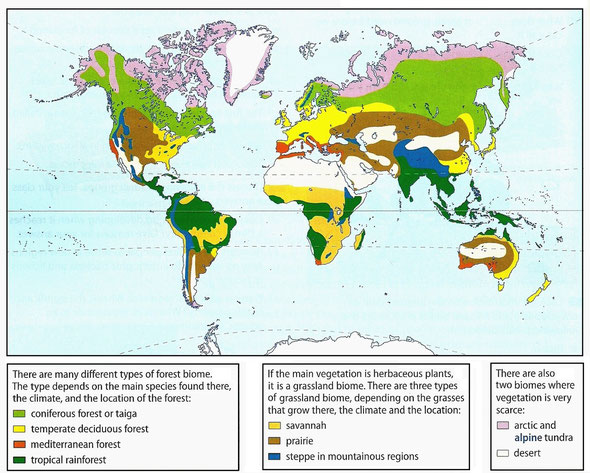
There are three large climate zones in each hemisphere:
- Frigid zone. It is the cold zone from the Poles to the polar circles.
- Polar desert
- Tundra (cold grassland)
- Taiga (Boreal forest)
- Temperate zone. It is the area between the polar circles and the tropics.
- Temperate forest
- Deciduous forest
- Mediterranean forest
and shrubland (Chaparral)
- Grasslands (temperate grassland)
- Steppe
- Prairie
- Torrid zone. It is the hot zone between the Tropic of Cancer
and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- Tropical rainforest
- Savannah (hot grassland)
- Hot desert
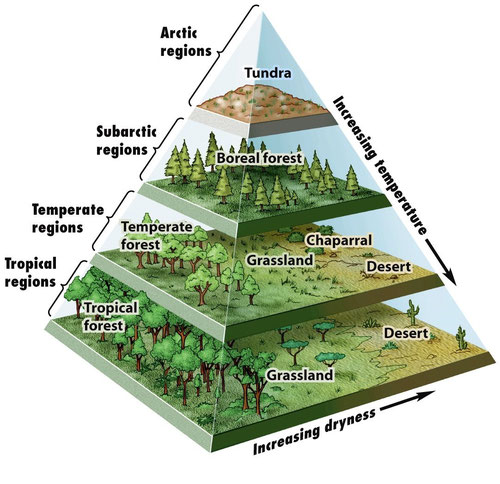
Animation: Biomes (McGraw Hill)

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
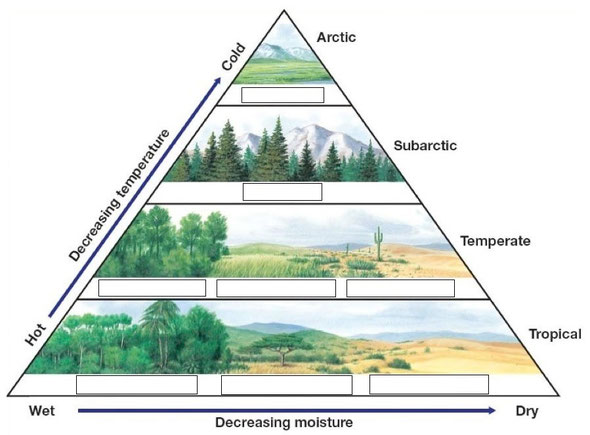
2.1. This sketch represents the distribution of terrestrial biomes. Indicate which
correspond to each one. What factors determine this distribution?
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




