4. Reptiles
It is estimated that there are about 8,200 species of reptiles.
Reptiles appeared more than 310 million years ago.
They evolved from a group of amphibians that developed impermeable skin
without glands, and eggs with shell that allow them leave wet environments.
a) Habitat
Reptiles are terrestrial tetrapods.
Most reptiles live in very dry environments, although some of them spend
a lot of time in water (e.g. crocodiles) and some are marines (e.g. tortoises).
b) Morphological characteristics
- They have four limbs, except snakes that do not have legs.
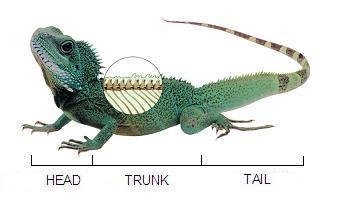
- Their body is divided into: head, trunk and tail.
- Their skin is thick and is covered by hard scales and does not have glands.
It protects them from water loss. Lizards and snakes shed their skin
and tortoises have a hard shell called carapace.
c) Vital functions:
Nutrition:
The digestive system is complete. They have a mouth, stomach, intestine and anus. It opens outside by the cloaca. Most are carnivorous. They have teeth to capture prey. Turtles do not have teeth but have beak. Many snakes have poisonous gland connected to fangs.
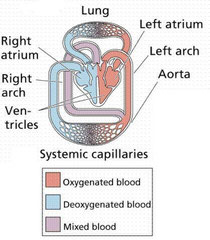
Reptiles breathe through lungs.
They have double circulation.
Their heart has four chambers:
two upper atriums and two lower
connected ventricles, so that
they have incomplete circulation.
This means that oxygenated blood
and deoxygenated blood mix.
They have two kidneys.
Interaction
They have a well-developed brain and sense organs: eyes (with eyelids), ears (without auricles), taste, smell and touch.
They are poikilotherms (cold-blooded).
This means that they can not keep their body temperature constant.
They adapt it to the environment temperature.
Reproduction:
Fertilization can be external or internal.
Most of them are oviparous. Some snakes are ovoviviparous.
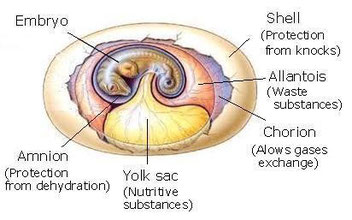
They lay eggs with a flexible shell and an internal impermeable membrane (amnion) that protect the embryo and allows laying them
out of water.
Usually, they do not incubate the eggs or take care of their young.
d) Classification:
- Chelonians (Turtles and tortoises)
Their body is covered by a carapace.
They don’t have teeth, but a beak.
Adults are mainly terrestrial and some are aquatic
(fresh water and marines)
- Crocodilians (Crocodiles. alligators and gavials)
Their body is elongated and large.
They live in aquatic environments (swamps and rivers)
All of them are carnivorous.
- Squamata
They live terrestrial environments.
All of them are carnivorous.
- Saurians (Lizards). They have four limbs
- Serpents (Snakes). They do not have limbs.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
4.1. Reptiles are poikilotherms or cold-blooded animals.
a. What does it mean?
b. In spite of this, many of them can control their body temperature
keeping it, higher or lower than the environment, with their behaviour.
Pictures represent a desert lizard in different day moments.

Describe it behaviour in each moment and explain what consequences
can it has in its body temperature.
A. At dawn, the lizard……………………………, as a result ………………………
B. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
C. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4.2. Listen and relate each sentence with the group of Reptiles it belongs to:
a. Chelonians
b. Crocodilians
c. Saurians
d. Serpents

Now,
check
your
answers!

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.

SPEAKING ACTIVITIES
Now, in turns with your partner,
answer the questions in the worksheet.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)





