2. The physical environment
Abiotic
factors are the variables of the physical environment (light, temperature, humidity, etc) that affect living beings.
The most important abiotic factors are:
- Temperature.
It has an enormous importance in the development of life.
Freezing occurs below certain temperature values and all cellular activity stops
above certain limits.
Temperature depends on altitude, latitude and the season or day hour.
Its influence is bigger in land than in water. Aquatic environments have usually
a constant temperature, while in terrestrial environments, temperature
changes a lot.
- Light
The amount of solar radiation that arrives to the plants depends on the altitude,
the latitude and the time of the year and the hour of the day.
For plants, light is essential to perform photosynthesis. On the other hand,
light affects animals’ sleep patterns and other biological activities.
It is difficult for light to penetrate an aquatic environment and it can only
enter until certain depth.
- Humidity
Water is essential for all living beings. The presence or absence of water or
the precipitations amount and its distribution determine the type of living beings
we can find in an ecosystem.
- Salinity
It is the concentration of salt in water. In aquatic environments, water can be
freshwater or salt water depending on the amount of salts it contains.
- Pressure
It does not vary very much with altitude in terrestrial environment
but it increases considerably with depth in aquatic environment.
The influence of the abiotic factors can be more or less intense depending on the environment:
- The most influential ones in terrestrial environment are temperature
and humidity.
- The most influential ones in aquatic environments are light, salinity
and pressure.
These factors determine the types of living beings which develop in an ecosystem. They have a tremendous impact because they influence the ecosystem in many ways. For example, climate or water supply, affects the behavior and the vital functions of the organisms.
Tolerance limits are the maximum or minimum values of a variable which a species can tolerate. When variables exceed these limits, organisms cannot survive. In this case, this factor is called limiting factor.

In order to survive, living beings adapt to their environment.
Adaptation is the progressive adjustment of a species to the special conditions of the environment where it lives.


Animation: Animal adaptations (Study jams)
Animation: Plant adaptations (Study jams)

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
2.1. Look at the graph showing the temperature tolerance for a species
and answer:
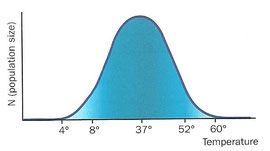
a. What is the zone of tolerance?
b. Which are the limits of tolerance?
c. Which temperature is the optimal?
2.2. Indicate what abiotic factor correspond each one of these adaptations:
a. Large leaves.
b. Fur and feathers.
c. Hibernation and migration
e. Storing of nutritive substances in roots
f. Reduced leaves or transformed into spines.
g. Skin with scales and without glands

Now,
check
your
answers!

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




